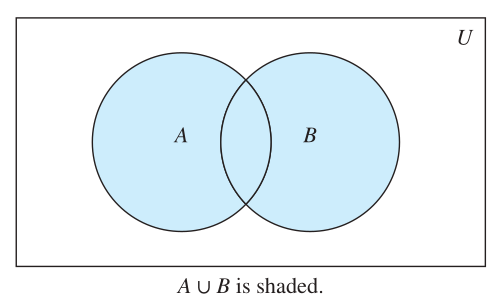
Union
- The union of the sets A and B, denoted by A ∪ B, is the set that contains those elements that are either in A or in B, or in both.
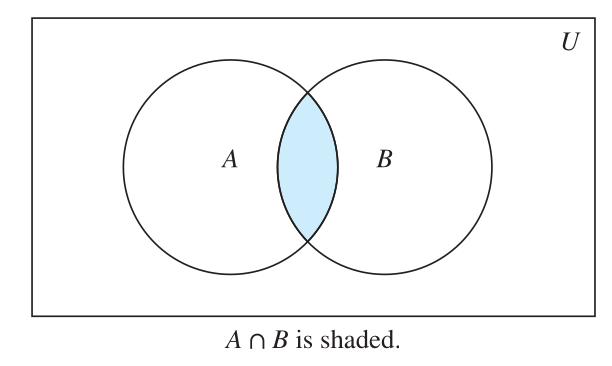
Intersection
- The intersection of the sets A and B, denoted by A ∩ B, is the set containing those elements in both A and B.
Disjoint
Two sets are called disjoint if their intersection is the empty set.
Principle of inclusion–exclusion
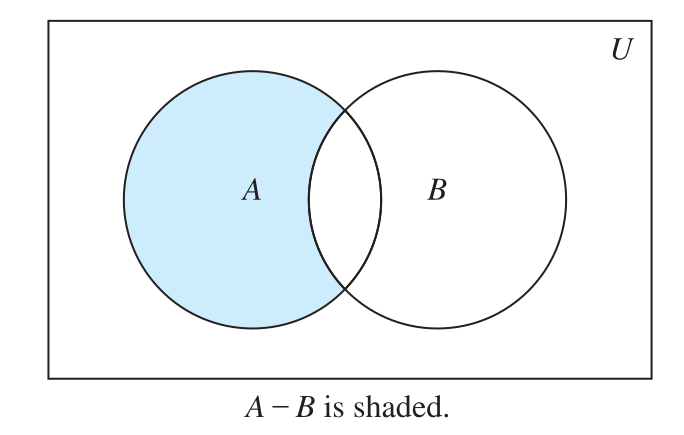
Difference
- The difference of A and B, denoted by A − B (A∖B), is the set containing those elements that are in A but not in B.
- The difference of A and B is also called the complement of B with respect to A.
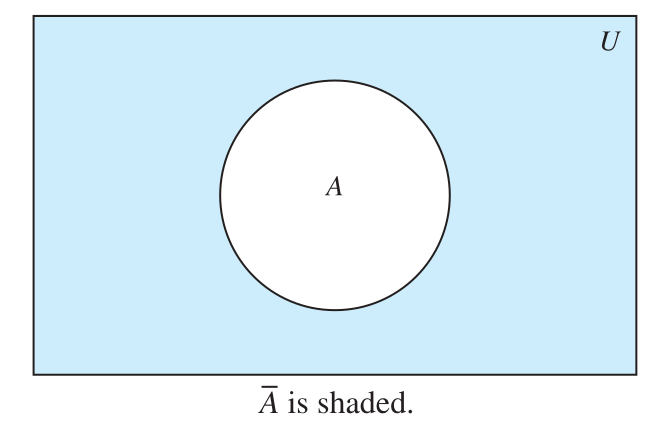
Complement
- Let U be the universal set. The complement of the set A, denoted by A, is the complement of A with respect to U.
- Therefore, the complement of the set A is U − A.
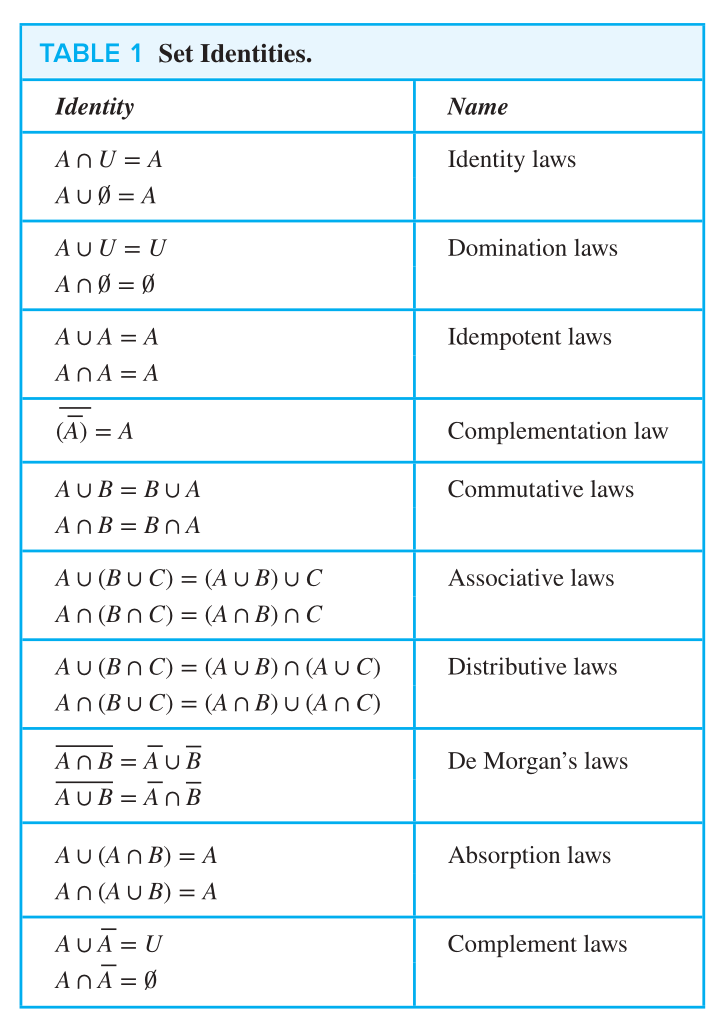
Set Identities
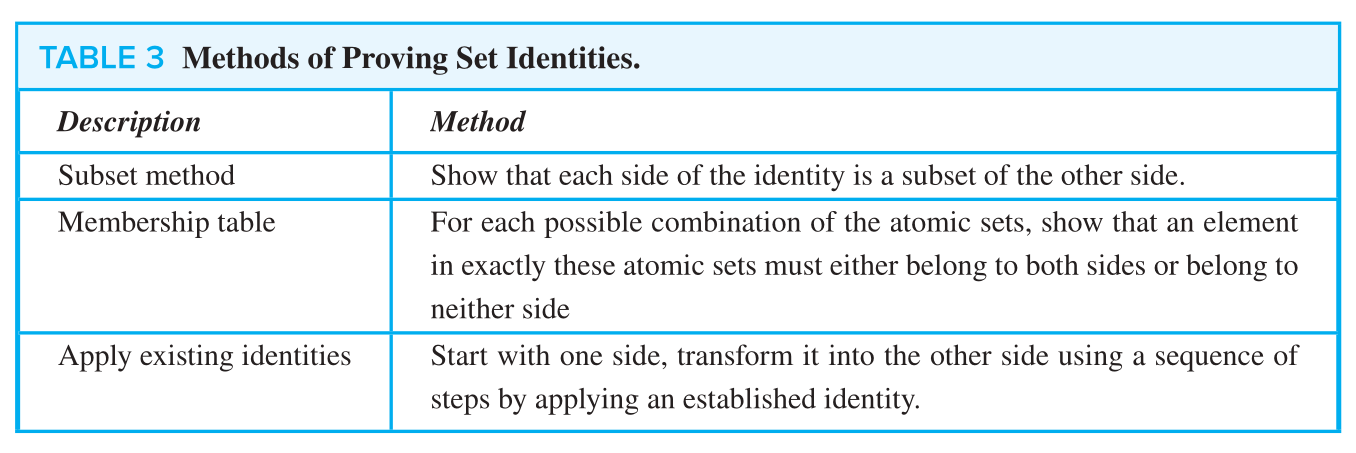
Methods of Proving Set Identities
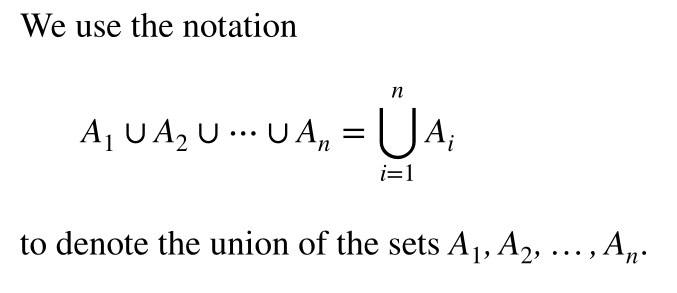
Generalized Unions and Intersections
The union of a collection of sets is the set that contains those elements that are members of at least one set in the collection.
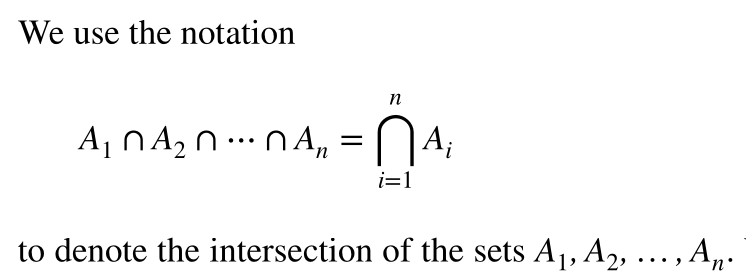
The intersection of a collection of sets is the set that contains those elements that are members of all the sets in the collection.
Computer Representation of Sets
- Assume that the universal set U is finite
- First, specify an arbitrary ordering of the elements of U, for instance
. - Represent a subset A of U with the bit string of length n where the
bit in this string is 1 if belongs to A and is 0 if does not belong to A - Ex:
- Let
What bit strings represent the subset of all odd integers in U ? - A =
- Bit strings:
- Let
Multiset
- The number of times that an element occurs in an unordered collection matters.
- A multiset (short for a multiple-membership set) is an unordered collection of elements where an element can occur as a member more than once
- Ex:
is the multiset that contains the element a thrice and the element b twice. Hence, where 3, 2 is called multiplicities
Union
- The union of the multisets P and Q is the multiset in which the multiplicity of an element is the maximum of its multiplicities in P and Q
Intersection
- The intersection of P and Q is the multiset in which the multiplicity of an element is the minimum of its multiplicities in P and Q.
Difference
- The difference of P and Q is the multiset in which the multiplicity of an element is the multiplicity of the element in P less its multiplicity in Q unless this difference is negative, in which case the multiplicity is 0
Sum
- The sum of P and Q is the multiset in which the multiplicity of an element is the sum of multiplicities in P and Q.