Sequences
- A sequence is a function from a subset of the set of integers (usually either the set
or the set ) to a set S - We use the notation
to denote the image of the integer n - We call
a term of the sequence (term = phần tử) - We use the notation
to describe the sequence
Geometric progression (Cấp số nhân)
- A geometric progression is a sequence of the form
- where the initial term
and the common ratio are real numbers. - In other words, A geometric progression is a discrete analogue of the exponential function
- Example:
- The sequences
with - a = 6
- r = 1/3
- The sequences
Arithmetic progression (Cấp số cộng)
- An arithmetic progression is a sequence of the form
- where the initial term
and the common difference are real numbers. - In other words, A arithmetic progression is a discrete analogue of the linear function
- Example:
- The sequences
with - a = -1
- d = 4
- The sequences
Recurrence Relations
- A recurrence relation for the sequence
is an equation that expresses in terms of one or more of the previous terms of the sequence , for all integers n with , where is a nonnegative integer - A sequence is called a solution of a recurrence relation if its terms satisfy the recurrence relation
- Example:
- Let
be a sequence that satisfies the recurrence relation for , and suppose that and - ⇒
,
- Let
- The
from the example is called initial conditions
Fibonacci sequence
- Initial conditions
- Recurrence relation
Closed formula
- We say that we have solved the recurrence relation together with the initial conditions when we find an explicit formula
- Example:
- Let
be a sequence that satisfies the recurrence relation for , and suppose that - ⇒
, the factorial function
- Let
Solve recurrence relations
Iteration
- Let
be a sequence that satisfies the recurrence relation for , and suppose that
Forward substitution
Backward substitution
Special Integer Sequences
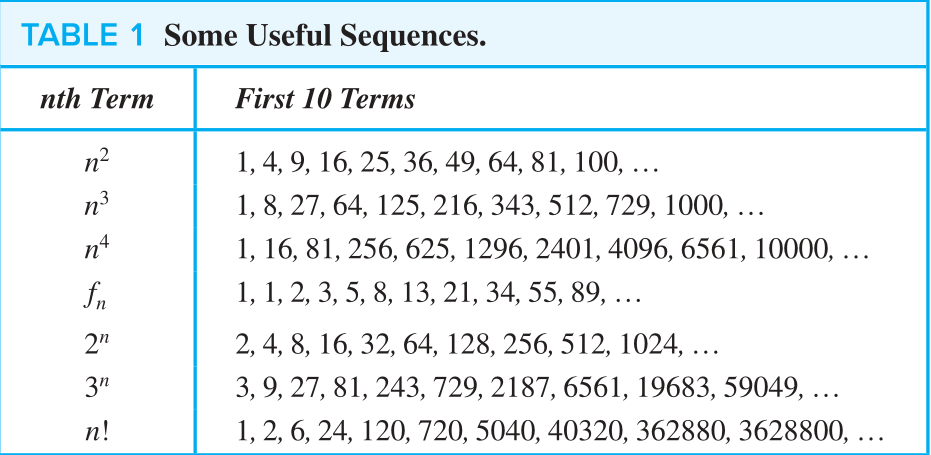
- Example:
- How can we produce the terms of a sequence if the first 10 terms are
? - ⇒
with initial conditions are ,
- How can we produce the terms of a sequence if the first 10 terms are