Primes
- An integer p greater than 1 is called prime if the only positive factors of p are 1 and p.
- A positive integer that is greater than 1 and is not prime is called composite, means if and only if there exists an integer a such that a ∣ n and 1 < a < n.
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic
🔑
Every integer greater than 1 can be written uniquely as a prime or as the product of two or more primes, where the prime factors are written in order of non-decreasing size.
Trial Division
Theorem 2
🔑
If n is a composite integer, then n has a prime divisor less than or equal to
- Proof:
- From composite def, we have
where b > 1 - Proof that
OR - Assume,
AND , then , contradict
- From composite def, we have
💡
From Theorem 2, it follows that an integer is prime if it is not divisible by any prime less than or equal to its square root
Theorem 3
💡
There are infinitely many primes
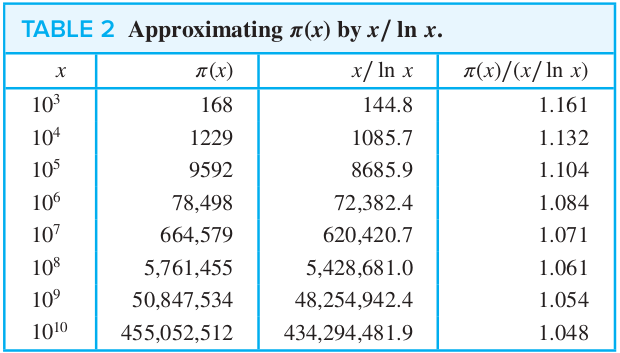
Theorem 4 (The prime number theorem)
💡
The ratio of
Mean that,
💡
Prime form
Greatest Common Divisors
- Let a and b be integers, not both zero. The largest integer d such that
and is called the greatest common divisor of a and b. The greatest common divisor of a and b is denoted by
Algorithm
- To find the
is to use the prime factorizations of these integers - Suppose we factorize a and b into,
- Then,
Least Common Multiples
- The least common multiple of the positive integers a and b is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both a and b. The least common multiple of a and b is denoted by
Algorithm
- Same as GCD but get
The relationship between GCD and LCM
💡
Let a and b be positive integers. Then
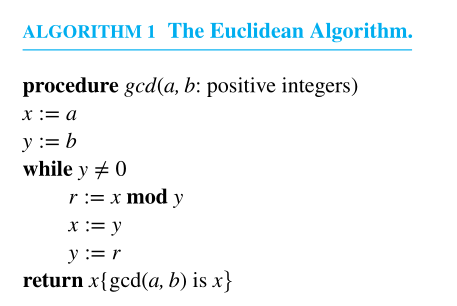
The Euclidean Algorithm
💡
An efficiency algorithm to find
✅
Let
gcds as Linear Combinations
BÉZOUT’S THEOREM
- If a and b are positive integers, then there exist integers s and t such that,
- This equation is called Bézout’s identity
- Two integers
and are called Bézout coefficients of a and b
LEMMA 2
✅
If a, b, and c are positive integers such that gcd(a, b) = 1 and a ∣ bc, then a ∣ c.
LEMMA 3
✅
If p is a prime and p ∣ a1 a2 ⋯ an , where each ai is an integer, then p ∣ ai for some i.
THEOREM 7
✅
Let m be a positive integer and let a, b, and c be integers.
If
⇒