TIP
Functions are sometimes also called mappings or transformations.
Function, domain, codomain, range
- Let A and B be nonempty sets.
- A function
from A to B is an assignment of exactly one element of B to each element of A. We write if is the unique element of B assigned by the function to the element of A. - If
is a function from A to B, we write
Where,
is the domain of (Tập xác định, TXĐ) is the codomain of (Tập giá trị / Tập đích)
If
, we say that b is the image of a and a is a preimage of b. (ảnh và nghịch ảnh) if f is a function from A to B, we say that f maps A to B. (ánh xạ)
A function
can also be defined in terms of a relation from A to B (just a subset of ) 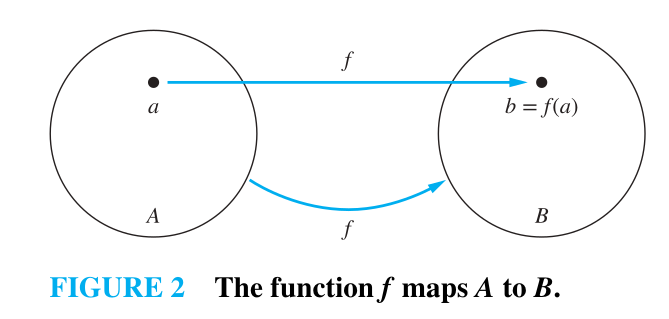
The range is the set of all values of
, and is always a subset of the codomain. In other words, range is actually created set. Example,
- Let
, , - Domain of f is all integers
- Codomain of f is all integers
- Range of f is
- Let
Function equality
- Two functions are equal when they have
- The same domain
- The same codomain
- Map each element of their common domain to the same element in their common codomain (tức là
với mọi a)
Sum and product
- Let
and be functions from . - Then
and are also functions from to defined by
Set of images
Let
Or, for shorthand
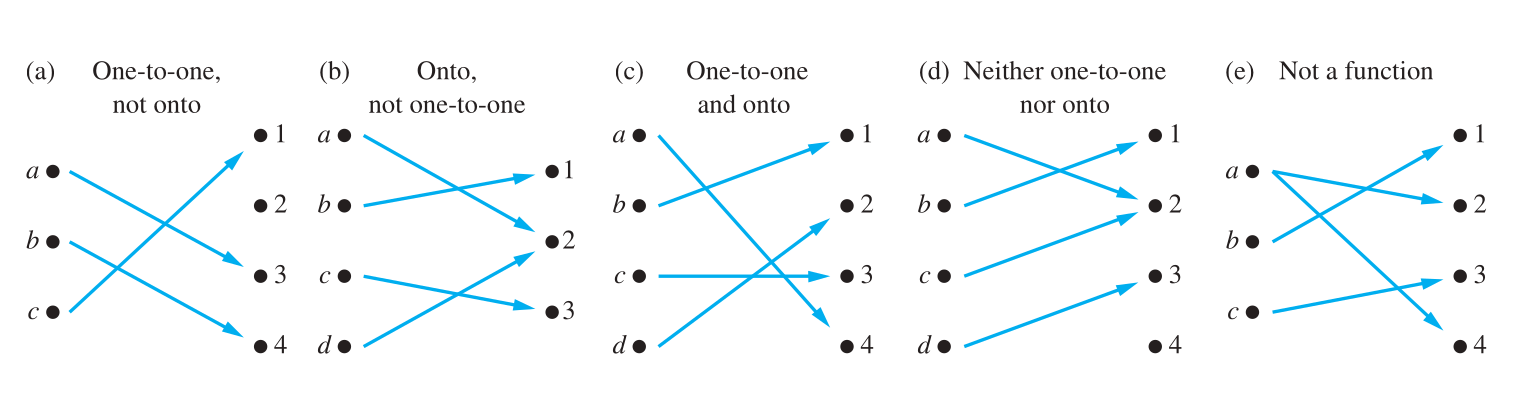
One-to-One and Onto Functions
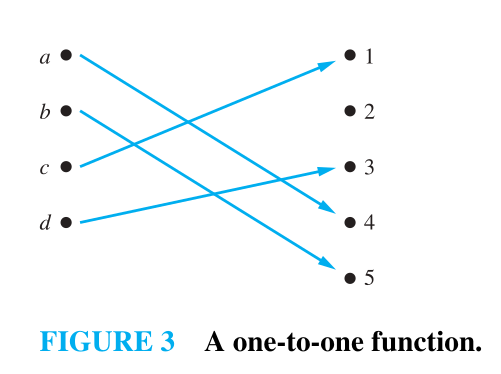
One-to-one (injective) function
- A function
is said to be one-to-one, or an injection, if and only if implies that for all a and b in the domain of . - A function is said to be injective if it is one-to-one.
- In other words,
- Note that a function f is one-to-one if and only if
whenever
- Note that a function f is one-to-one if and only if
- We can express that f is one-to-one using quantifiers
Or using contrapositive,
- Example:
- The function
with domain is one-to-one with domain is one-to-one
- The function
Increasing/decreasing functions
- Hàm đồng biến/ nghịch biến
- A function
whose domain and codomain are subsets of the set of real numbers is called increasing if , and strictly increasing if , whenever and x and y are in the domain of f. Hence
- Similarly, for decreasing functions
TIP
If a function either strictly increasing or strictly decreasing ⇒ that function is one-to-one
If a function either increasing or decreasing ⇒ that function is not one-to-one
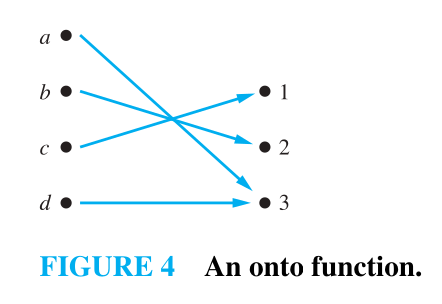
Onto (surjective) function (Hàm toàn)
- For some functions the range and the codomain are equal
- A function f from A to B is called onto, or a surjection, if and only if for every element
there is an element with . - A function f is called surjective if it is onto.
Bijective function (Hàm song ánh)
- The function f is a one-to-one correspondence, or a bijection, if it is both one-to-one and onto.
- We also say that such a function is bijective.
Function Key Takeaway

Inverse Functions and Compositions of Functions
Inverse function
- Let f be a one-to-one correspondence from the set A to the set B.
- The inverse function of f is the function that assigns to an element b belonging to B the unique element a in A such that f (a) = b.
- The inverse function of f is denoted by
. Hence, when
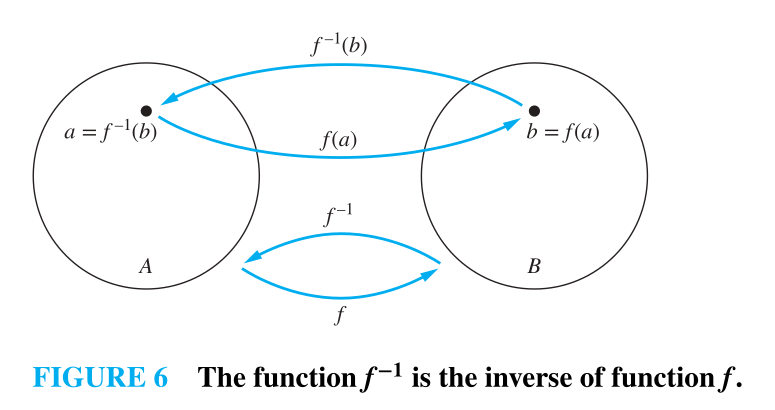
TIP
A one-to-one correspondence is called invertible because we can define an inverse of this function.
A function is not invertible if it is not a one-to-one correspondence, because the inverse of such a function does not exist.
Composition functions
- Let
be a function from the set A to the set B and let be a function from the set B to the set C. The composition of the functions f and g, denoted for all by , is the function from A to C defined by
- Domain of
is domain of - Range of
is image of the range of with respect to the function - To find
we first apply the function g to a to obtain and then we apply the function f to the result to obtain
TIP
The composition
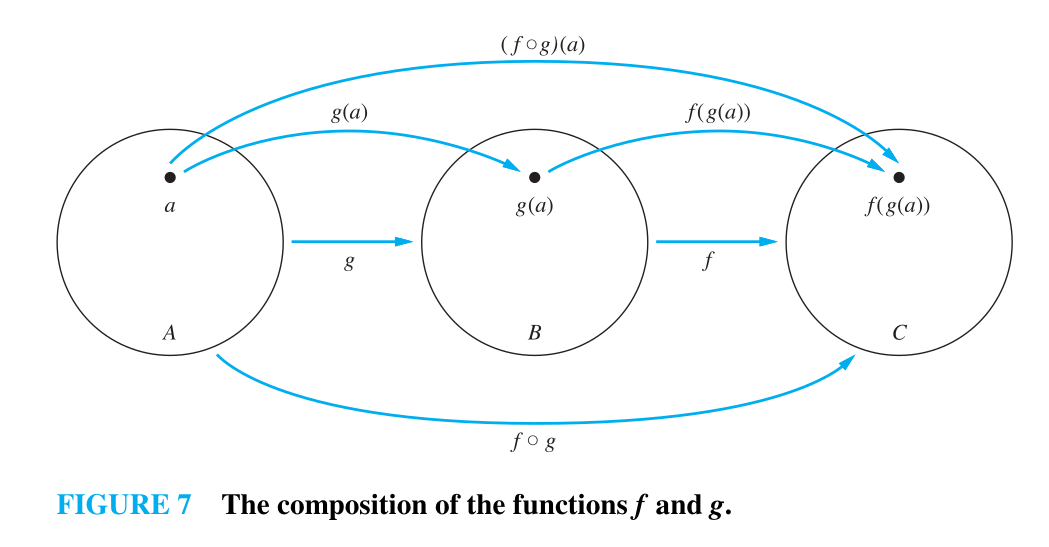
TIP
The Graphs of Functions (Đồ thị)
- Let f be a function from the set A to the set B. The graph of the function f is the set of ordered pairs
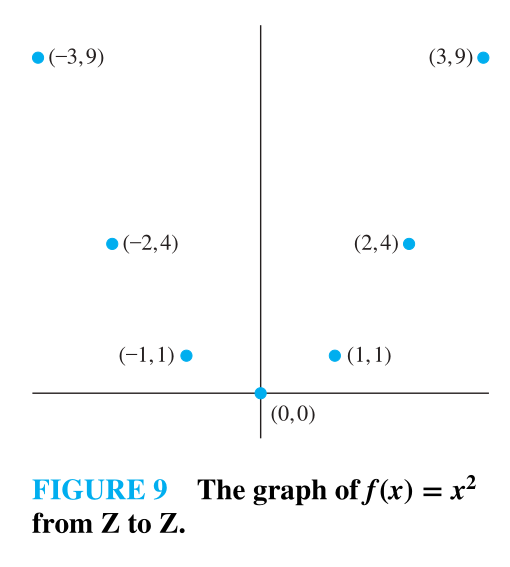
Some Important Functions
Floor function
- The floor function assigns to the real number x the largest integer that is less than or equal to x. The value of the floor function at x is denoted by
Ceiling function
- The ceiling function assigns to the real number x the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to x. The value of the ceiling function at x is denoted by
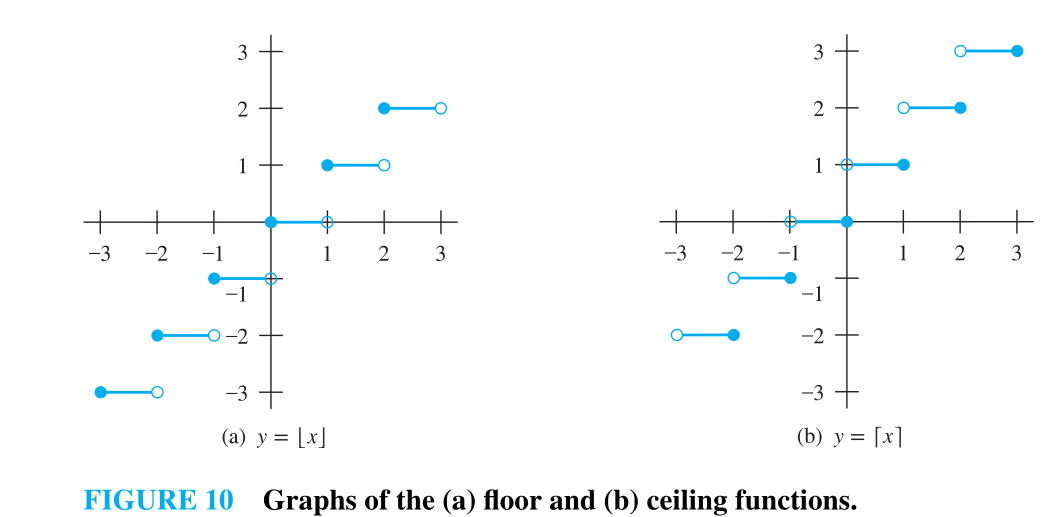
Useful properties of floor and ceiling functions
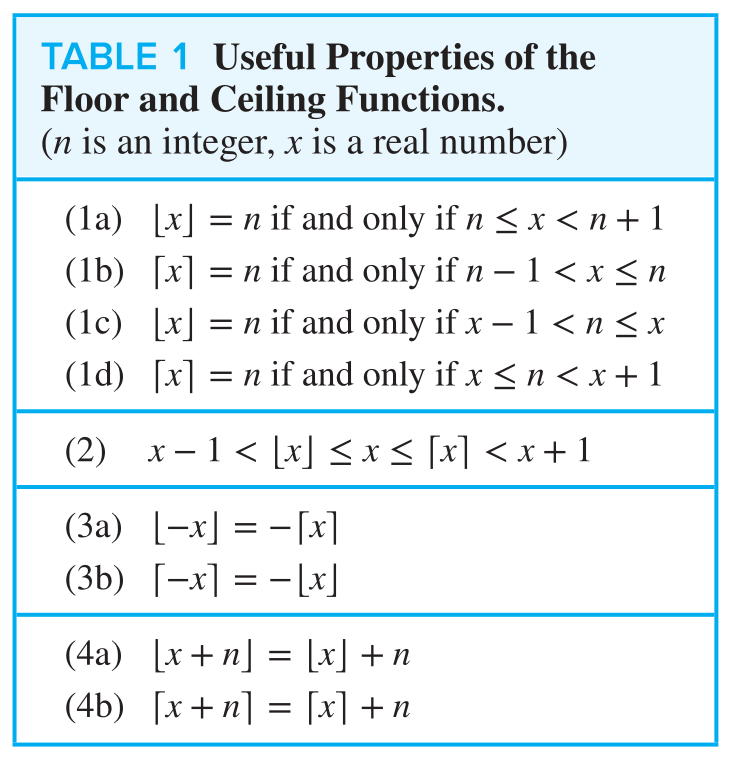
- A useful approach for considering statements about the floor function is to let
, where is an integer, and , the fractional part of x, satisfies the inequality - Similarly, when considering statements about the ceiling function, we have
Partition functions (hàm từng phần)
- Chỉ định nghĩa trên một phần của tập A (không phải tất cả)
- Example:
- undefined at x = 0, ⇒ partial function
Total functions (hàm toàn phần)
- Được định nghĩa cho mọi phần tử trong A. Không bỏ sót phần tử nào.